
Course: MS Thesis Research
Duration: August 2014 - December 2016
Collaborators: Zhenhuan Xu, Alex Bruce, Prahlad Kulkarni, Javieradrian Ruiz, Michael Woodworth, Claire Lang
Advisor: Prof. Amy Marconnet & John Howarter
Funding Agency: Cooling Technologies Research Center
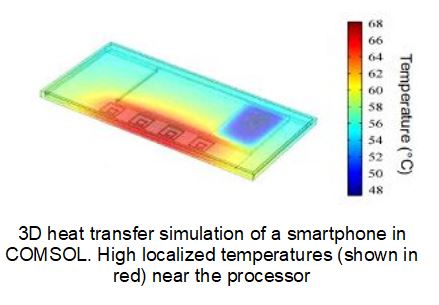
Electronic devices keep getting more powerful and smaller in size. The temperature limits for reliable operation of the materials used to make phones (Ex: Silicon used in processor ) remain unchanged.
Cooling a mobile phone implies developing a thermal management solution with the following challenges:
The outer case or surface temperature of the phone should be < 40°C so that the user can hold the phone
The processor temperature should be < 80°C for reliable operation
Heat transfer to the ambient is limited by natural convection. In other words, the phone is not used in a “windy” environment.
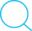
Many interactive smartphone applications have a short burst of excess power consumption followed by an idle time waiting for user inputs. Keeping the processor temperature within operating limits goes a long way in ensuring a responsive user interface (preventing lags).
Store heat without increasing the temperature (around their melting point). The supplied heat is absorbed and used to change the phase. Conversely, during solidification, heat is liberated and the material changes phase to solid.
From a thermal management standpoint, this is like hitting a jackpot!
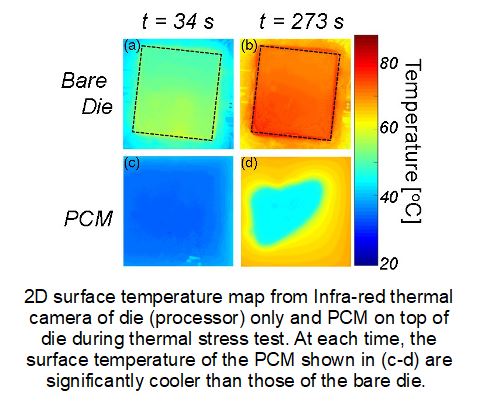
A PCM can be used to absorb the excess heat during periods of intense use in a smartphone while keeping the temperatures around the melting point. This is a win-win situation since the smartphone performance is improved while keeping the (processor & surface) temperatures in check.
How can PCMs be used to deliver an optimal cooling solution? I conducted a feasibility study on the use of PCMs in smartphones to answer the following questions.
| Questions | Work Done |
|---|---|
| How to compare different thermal solutions? |
|
| What are the key design parameters? |
|
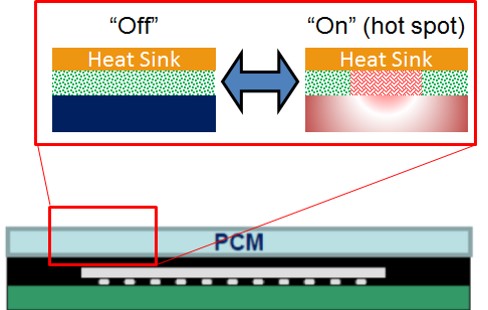
| What are the critical material properties? |
|
| How do they influence the key design parameters? | Analyzed the effect of material properties, PCM weight and integration location on the cutoff time by
|
Achieved an increase in cutoff time by \(1.5 - 2.48 \times\) with the PCM compared to no PCMs
PCM thickness and convection heat transfer coefficient have the largest impact on the cutoff time
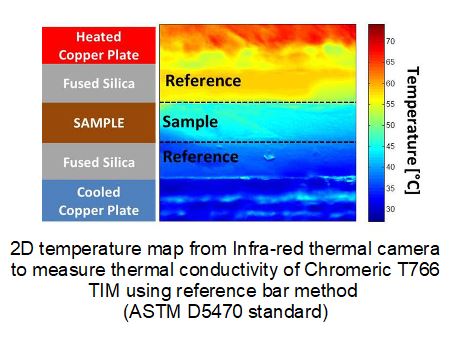

PCM Melt Front Propagation
MS Thesis: Passive Thermal Management using Phase Change Materials
International Journal of Thermal Sciences: Experimental Investigation of Phase Change Materials for Thermal Management of Handheld Devices
ASME InterPACK 2015 Conference: Passive Thermal Management Using Phase Change Materials: Experimental Evaluation of Thermal Resistances
Design space exploration
Thermal Design
MATLAB programing and scripting to extract and analyze data
2D/3D heat transfer/CFD simulations in COMSOL, ANSYS ICEPAK
Hardware thermal testing
3D Printing
IR Camera & thermocouples temperature measurement
Mentoring undergraduate students